Changing Themes Dynamically Using JSON
In this article, we will delve into how JSON can be leveraged to implement dynamic themes for a webpage. This approach eliminates the need to directly modify CSS files, making the theme management system more flexible, scalable, and easier to maintain.
Objective
Our goal is to create a webpage that dynamically switches between light and dark themes based on the sunrise and sunset times of the user’s location. We will use JSON to define the style configurations for each theme, which will then be applied dynamically via JavaScript .
Project Overview
The project consists of the following key files:
index.html– The structure of the webpage.style.css– Basic styling and transitions.app.js–JavaScriptto handle theme management and interaction.themes.json–JSONconfiguration for the theme styles.
Below, we will explore the content of each file in detail.
1. HTML File: index.html
This file contains the HTML structure of the webpage. It includes placeholders for the content, a button for manual theme switching, and a link to external JavaScript and CSS files.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Dynamic Theme Based on Sunrise and Sunset</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
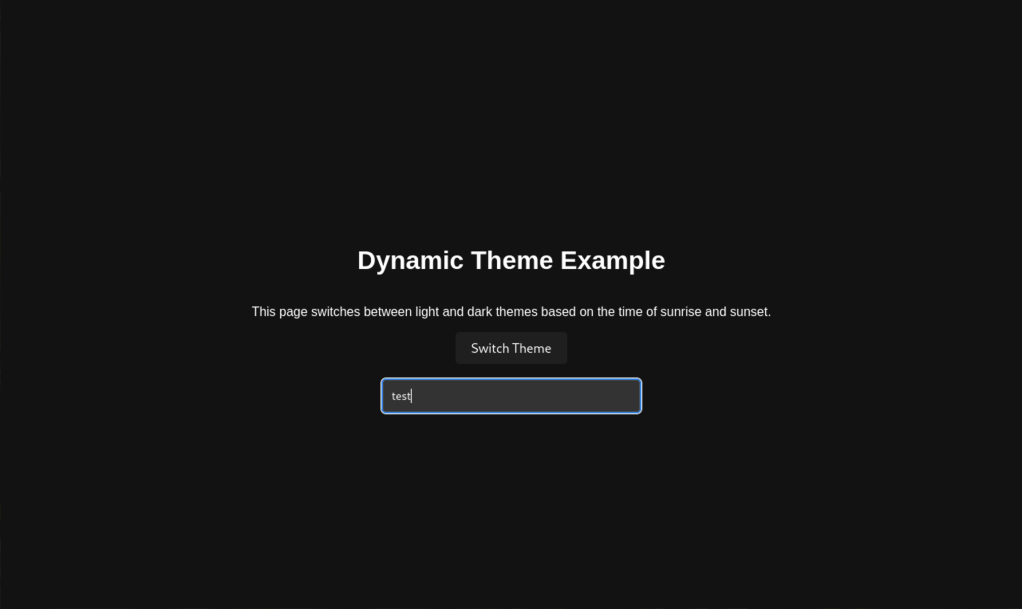
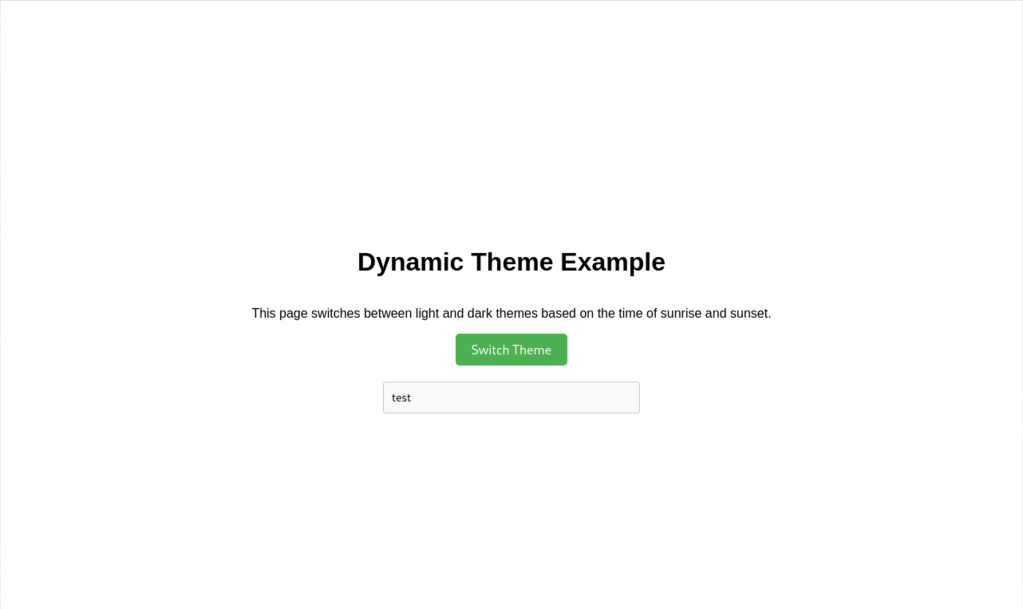
<h1>Dynamic Theme Example</h1>
<p>This page dynamically switches between light and dark themes based on the time of sunrise and sunset at your location.</p>
<button id="themeSwitcher">Switch Theme</button>
<input type="text" class="textbox" placeholder="Type something...">
<script src="app.js" defer></script>
</body>
</html>
2. CSS File: style.css
This file defines the default styling for the webpage and ensures smooth transitions between themes. The styles are intentionally generic, as the detailed theme-specific styles are defined in the JSON configuration.
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f0f0f0; /* Default background */
color: #000; /* Default text color */
margin: 0;
padding: 20px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
height: 100vh;
transition: background-color 0.3s ease, color 0.3s ease;
}
button {
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 16px;
cursor: pointer;
border: none;
border-radius: 5px;
transition: background-color 0.3s ease, color 0.3s ease;
}
input.textbox {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 14px;
margin-top: 20px;
border-radius: 4px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
width: 300px;
transition: background-color 0.3s ease, border-color 0.3s ease;
}
3. JavaScript File: app.js
The JavaScript file contains the logic for detecting the user’s location, fetching sunrise and sunset times, and dynamically applying themes based on the JSON configuration.
// Function to retrieve user’s location
function getUserLocation() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (navigator.geolocation) {
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(
(position) => resolve(position.coords),
(error) => reject(error)
);
} else {
reject(new Error("Geolocation is not supported by this browser."));
}
});
}
// Function to fetch sunrise and sunset times using an API
async function fetchSunTimes(lat, lng) {
const response = await fetch(`https://api.sunrise-sunset.org/json?lat=${lat}&lng=${lng}&formatted=0`);
const data = await response.json();
return {
sunrise: new Date(data.results.sunrise),
sunset: new Date(data.results.sunset),
};
}
// Function to determine the theme based on current time
function determineTheme(sunTimes) {
const now = new Date();
return now >= sunTimes.sunrise && now < sunTimes.sunset ? "light" : "dark";
}
// Function to apply a theme to the webpage
function applyTheme(theme, config) {
for (const element in config[theme]) {
const styles = config[theme][element];
document.querySelectorAll(element).forEach(el => {
for (const property in styles) {
el.style[property] = styles[property];
}
});
}
}
// Initialize the theme when the page loads
async function initializeTheme() {
try {
const coords = await getUserLocation();
const sunTimes = await fetchSunTimes(coords.latitude, coords.longitude);
const themeConfig = await fetch('themes.json').then(res => res.json());
const theme = determineTheme(sunTimes);
applyTheme(theme, themeConfig);
setupThemeSwitcher(themeConfig);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error initializing theme:", error);
}
}
// Function to set up manual theme switching
function setupThemeSwitcher(config) {
let currentTheme = "light"; // Default theme
document.getElementById("themeSwitcher").addEventListener("click", () => {
currentTheme = currentTheme === "light" ? "dark" : "light";
applyTheme(currentTheme, config);
});
}
initializeTheme();
4. JSON File: themes.json
The JSON file contains the styling details for both light and dark themes. This structure allows for easy modifications and the addition of new themes without altering the CSS or JavaScript code.
{
"light": {
"body": {
"backgroundColor": "#ffffff",
"color": "#000000"
},
"button": {
"backgroundColor": "#4CAF50",
"color": "#ffffff"
},
"input": {
"backgroundColor": "#f9f9f9",
"borderColor": "#ccc",
"color": "#000000"
}
},
"dark": {
"body": {
"backgroundColor": "#121212",
"color": "#ffffff"
},
"button": {
"backgroundColor": "#1f1f1f",
"color": "#ffffff"
},
"input": {
"backgroundColor": "#333333",
"borderColor": "#444444",
"color": "#ffffff"
}
}
}
Advantages of Using JSON for Themes
- Flexibility: Themes can be easily modified or added without altering
CSSorJavaScriptfiles. - Scalability:
JSONstructures can accommodate multiple themes and complex configurations. - Maintainability: Centralized theme definitions reduce redundancy and improve organization.
Conclusion
By leveraging JSON , we can create a powerful and flexible system for managing dynamic themes in a web application. This approach not only simplifies theme management but also enhances the user experience by responding dynamically to environmental conditions. Try implementing this project and customize it to suit your needs!